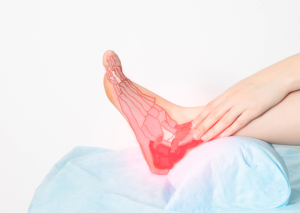
The Impact of Sprains and Strains on Basketball Performance
In the world of basketball, where agility, speed, and precision are paramount, injuries such as sprains and strains can have a profound impact on an athlete's performance. This article exploresRead More